This web page was produced as an assignment for Gen677, an undergraduate course at UW-Madison Spring 2009
What do we know about the proteins SORL1 interacts with?
Two proteins that SORL1 interacts with appear to be key players in the progression of AD. APP is the precursor to amyloid-beta plaques and is shuffled by SORL1 into either the recycling pathway or the late endosomal pathway. Additionally, BACE is is the protein that actually cleaves APP once it begins down the late endosomal pathway. The information below was generated through searches on GeneCards.
BACE1 (beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme 1)

Cytogenetic location: 11q23.2-q23.3
Size: 30,559 base pairs and 501 amino acids
Isoforms: 4
Gene Ontology Terms: membrane fraction, endosome, Golgi apparatus, integral to plasma membrane, membrane, axon, cytoplasmic vesicle, aspartic-type endopeptidase activity, beta-aspartyl-peptidase activity, beta-amyloid metabolic process, and membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis.
The picture above is of the protein domains of BACE1 isoform C (from SMART). All four of the isoforms had the exact same layout. It is curious that the only domain to show up is a transmembrane domain as we already know that BACE1 proteolytically cleaves APP. I expected more to be predicted about the BACE1 protein domains.
Because we know that BACE1 cleaves APP, which leads to AD plaque build up, BACE1 is an intuitive target for RNAi or knockout experiments in AD models. Witht his in mind, I looked for RNAi phenotypes through Phenobank, RNAi database, and FLYRNAi.org. Unfortunately nothing was available through Phenobank, and I was unable to find a fly homolog closely related enough to BACE1 that I was comfortable using. Regardless, I believe this information could be quite interesting and valuable in the future.
Size: 30,559 base pairs and 501 amino acids
Isoforms: 4
Gene Ontology Terms: membrane fraction, endosome, Golgi apparatus, integral to plasma membrane, membrane, axon, cytoplasmic vesicle, aspartic-type endopeptidase activity, beta-aspartyl-peptidase activity, beta-amyloid metabolic process, and membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis.
The picture above is of the protein domains of BACE1 isoform C (from SMART). All four of the isoforms had the exact same layout. It is curious that the only domain to show up is a transmembrane domain as we already know that BACE1 proteolytically cleaves APP. I expected more to be predicted about the BACE1 protein domains.
Because we know that BACE1 cleaves APP, which leads to AD plaque build up, BACE1 is an intuitive target for RNAi or knockout experiments in AD models. Witht his in mind, I looked for RNAi phenotypes through Phenobank, RNAi database, and FLYRNAi.org. Unfortunately nothing was available through Phenobank, and I was unable to find a fly homolog closely related enough to BACE1 that I was comfortable using. Regardless, I believe this information could be quite interesting and valuable in the future.
APP (Amyloid beta A4 protein precursor)
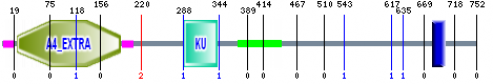
Cytogenetic location: 21q21.3
Size: 290,272 base pairs and 751 amino acids
Isoforms: 3
Gene Ontology Terms (abbreviated list): golgi apparatus, axon, neuromuscular junction, neuron projection, metal ion binding, serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity, adult locomotory behavior, visual learning, neuron remodeling, dendrite development, collateral sprouting in the absence of injury, and neuromuscular process.
The picture above is from SMART and represents the protein domains of APP isoform B. The KU (BPTI/Kunitz family of serine protease inhibitors) domain may be of some interest to AD. According to SMART, this domain is found in the alternatively spliced forms of AD amyloid-beta protein (the direct precursor to the plaques). I believe this warrants further investigation into the various isoforms of APP and how the KU domain is preserved, modified, or cleaved as APP is processed.
Size: 290,272 base pairs and 751 amino acids
Isoforms: 3
Gene Ontology Terms (abbreviated list): golgi apparatus, axon, neuromuscular junction, neuron projection, metal ion binding, serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity, adult locomotory behavior, visual learning, neuron remodeling, dendrite development, collateral sprouting in the absence of injury, and neuromuscular process.
The picture above is from SMART and represents the protein domains of APP isoform B. The KU (BPTI/Kunitz family of serine protease inhibitors) domain may be of some interest to AD. According to SMART, this domain is found in the alternatively spliced forms of AD amyloid-beta protein (the direct precursor to the plaques). I believe this warrants further investigation into the various isoforms of APP and how the KU domain is preserved, modified, or cleaved as APP is processed.
References
Website Content and Design by Luke Lopas
Email: [email protected]
Last Updated 5/13/09
Genetics 677 Homepage
Email: [email protected]
Last Updated 5/13/09
Genetics 677 Homepage
